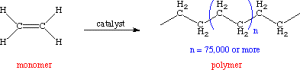
Polymerization
Definition
A polymer is a substance made up of many repeating units (called monomer units). Polymers are usually distinguished by a high molar mass (formula weight), often ranging into thousands or millions of grams per formula unit.
Polymerization is the process by which monomers (smaller chemical units) are combined to form a polymer. Polymerization is a poly-reaction of a monomer compound which molecule contains double bondings or rings The poly-reaction can occure under following conditions:
Triggered by
The polymerization can be triggered by the following factors
- Initiator (reaction partner)
- Heat
- Light
- Radiation
Some unsaturated compounds with one or more double bonds are able to polymerise.
- Vinyl compounds
- Vinylidene compounds
- Acrylic compounds
- Carbonyl compounds
- Styrene
- Ethylene Oxide; Propylene Oxide
- Ethylene, Propylene, Isobutylene, Butadiene and Isoprene
Example
Ethylene (C2H4) is a highly flammable gaseous molecule with a formula weight (molar mass) of 32 grams per mol. When polymerized using a catalyst, it forms an insoluble solid comprised of straight chains of CH2 units called polyethylene. Polyethylene is a widely used commodity plastic.