Chloride test
The Chloride test is used to identify the presence of inorganic chlorides on the cargo tank bulkheads. Inorganic chloride wall wash specifications may vary from 0.1 ppm to 5 ppm depending on the requirements of the charterer and the sensitivity of the next cargo.
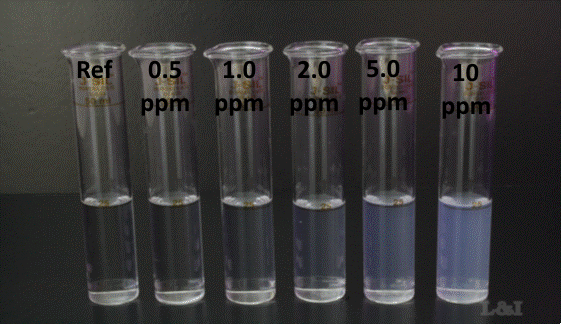
Inorganic chlorides react with silver nitrate to produce silver chloride, which forms an insoluble white precipitate. The amount of the precipitate is directly related to the concentration of inorganic chloride in the wall wash sample. By comparing the wall wash sample against a series of standards with known concentrations of inorganic chloride, (treated with silver nitrate in the same way as the wall wash samples), makes it possible to accurately determine the inorganic chloride content of the wall wash sample, even at low levels.
EQUIPMENT
- Nessler tubes 100 ml.
- Distilled water chloride free
- Pure laboratory Methanol (Acetone must not be used because it does not dissolve chlorides)
- Silver nitrate/nitric acid solution. Typically 2 – 5% silver nitrate in 10 – 20% nitric acid.
- Standard chloride solution (100mg/L or ppm) ()
PROCEDURE
Fill a Nessler tube with 25 ml of the wall wash sample and add 75 ml chloride free distilled water. Fill a second Nessler tube with 25-ml pure laboratory Methanol and add 75 ml distilled chloride free water (reference sample). Add to both tubes 5 drops of the Silver nitrate/nitric acid solution. Insert the stoppers, invert the tubes and leave to stand for 15 minutes out of direct sunlight.
Visually check if any turbidity is formed in the test sample by comparing it directly against the reference sample, by looking down through the length of the liquid in the Nessler tubes onto a black or dark background. Detection can be enhanced by carrying out this comparison in a darkened room and shining a wide beam flashlight, positioned about 30cm from the side of the tubes, through the bottom of the Nessler tubes.
RESULT
The presence of any turbidity signifies the presence of inorganic chlorides in the wall wash sample. In order to approximately quantify this, inorganic chloride standards should be prepared, as follows:
Add 1ml of the 100mg/L inorganic chloride standard to one 100ml Nessler tube. Add 25ml of laboratory pure methanol and then make up to the 100ml mark with chloride free distilled water. This standard is equal to 1mg/L or 1ppm inorganic chloride. Each additional ml of the 100mg/L inorganic chloride standard added to the Nessler tube will increase the concentration of the standard by 1mg/L or 1ppm, for example:
2ml of the 100mg/L inorganic chloride standard + 25ml of laboratory pure methanol + 73ml of chloride free distilled water = 2mg/L or 2ppm inorganic chloride.
5ml of the 100mg/L inorganic chloride standard + 25ml of laboratory pure methanol + 70ml of chloride free distilled water = 5mg/L or 5ppm inorganic chloride.
Add 5 drops of the silver nitrate solution to the prepared standards, stopper the tubes, invert and then leave to stand for 15 minutes out of direct sunlight. Visually compare the turbidity in the standards against the turbidity in the wall wash samples.
CALCULATION
Determine the inorganic chloride content of the wall wash sample by matching it as closely as possible to the prepared standards, bearing in mind the wall wash specification that applies to the next cargo. If the wall wash specification is maximum 1mg/L inorganic chloride, it is recommended to prepare a 1mg/L inorganic chloride standard and check that all wall wash samples have less turbidity than this standard. If they have more turbidity, the wall wash sample contains more than 1mg/L inorganic chloride and will fail to meet the requirements of the wall wash inspection.
NOTES
The most effective method for reducing inorganic chloride levels inside the cargo tanks, is to flush with copious amounts of chloride free water e,g. de-ionised water, which can prepared on board using DI water filters / resins or bought ashore. Another method for removal of inorganic chlorides is steaming, providing the steam has a sufficiently low inorganic chloride content.
Please also note that shore supplied freshwater can contain hundreds of ppm of inorganic chlorides and even freshwater produced on board from the evaporation of steam condensate can also contain up to 10ppm inorganic chlorides.
Colour Scale